Cage inserts for autoclaves
For particularly small (e.g. creamer) as well as non-stackable containers (e.g. pouches) however, so-called cage inserts, sometimes referred to as „baskets“, „carriers“ or „trays“, are used for safe placement in the autoclave. In addition to some standard shapes, special designs are always possible, which are tailored exactly to the respective product.
Which kind of cage inserts is suitable for which product respectively for which sterilization method?
Smaller products are often transported as bulk material directly from the sealer into the inserts. These are usually simple baskets (Figure 1), of which 2-4 are usually stacked in the cage. Here, the inserts serve less a position fixation for the individual product as an improvement of the handling.

Fig. 1 Small cream bowls as bulk material
For larger containers, flat trays are generally used, whose required height depends on the product. If these containers are sterilized in a stand-alone autoclave, simple trays without intermediate subdivisions usually suffice completely (Figure 2).

Fig. 2 Stainless steel-wire tray without subdivisions

Fig. 3 Tray made from perforated stainless steel sheet, with subdivisions
For rotary processes, however, it is advisable to use subdivisions / partitions, either with struts (Figure 3), annular supports (Figure 4) or trough-shaped recesses (Figure 5), in order to give each product a specific space and spacing for optimum flow during rotary sterilization. For foil dishes and pouches in many shapes, sizes and materials, customized trays can be made.

Fig. 4 Annular support for foil dishes

Fig. 5 Tray made from perforated stainless steel sheet with trough-shaped recesses for product placement
How can cage inserts best be placed inside the autoclave?
The simplest and cheapest solution here is the use of stackable inserts directly in the cage (Figure 6). This makes sense especially if you want to use the cages partly for stable containers, which are placed directly in the cage completely without inserts, only separated by spacer mats.
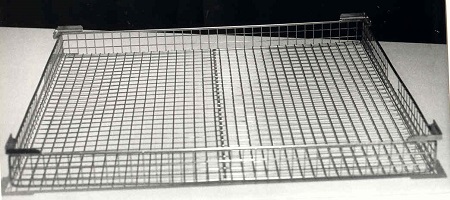
Fig. 6 Stainless steel wire-tray, stackable directly in the cage
However, trays can also be inserted in so-called “rack-cages” (Figure 7) with guide rails. This solution offers a particularly convenient loading and is suitable if the trays used are always the same, at least in height.
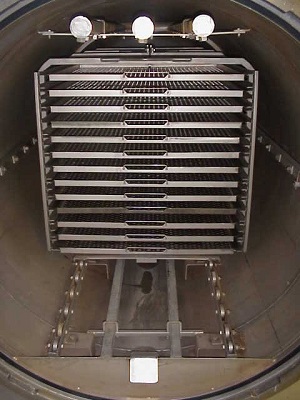
Fig. 7 “Rack-Cage” with guide rails and inserted trays
Special, stackable trays can be loaded directly into the autoclave as a closed package, even without a cage (Figure 8). Clever shaping makes even large parcels safely manageable and can be used in automated systems without problem. In case of manual cage loading, there are also cages available, whose side walls can (partially) be folded down (Figure 9).

Fig. 8 Stack of trays for direct loading into the autoclave

Abb. 9 Autoclave cage with side wall partially folded down
Which material should be used for cage inserts?
Cage inserts can basically be made from galvanized, perforated sheet, stainless steel wire mesh, perforated stainless steel sheet or plastic (e.g. PP, PPH). While baskets made of galvanized perforated plate are rarely used (mostly for full-water autoclaves made from boiler plate, stainless steel inserts are the rule today. Stainless steel wire-mesh trays (see Figure 2) are cost-effective, have the disadvantage, however, that pressure traces can be left on sensitive containers. Trays made of perforated stainless steel late, therefore are the most frequently used (Figure 10).
Plastic trays are a major exception (Figure 11). Their advantages (lower weight, possibility designing the compartments yourself due to plug-in system) are usually offset by the disadvantages in price (production in the expensive injection molding process) and in stability (suitable only for light products.

Fig. 10 Tray made from perforated stainless Steel sheet

Fig. 11 Tray made from plastic
